Deploy Azure Static Web Apps via Terraform
Date published:
In this blog post, I will show you how to deploy Azure Static Web apps using terraform for your static web application. According to Microsoft, Static Web Apps allows you to develop web apps quickly and easily with a static front-end and backend. The static web apps provide free SSL certificates, customised domains to your app, and integration using Azure Functions.
Setup
- Azure account
- Terraform installed
- Az CLI installed
Once the AZ CLI install, run az login and authenticate to Azure. It will direct automatically to log in to Azure with a login page. Once you have logged in, return to the terminal.
Create Backend Storage Account
Creating Backend state file - This step will make the necessary resources required to store the backend state file using the Azure storage account.
|
|
After you have successfully set up your backend state file in Azure. We will start looking into creating the Azure web apps.
Use Terraform to create Azure Resources
This is the terraform code to deploy a resource group, azure static web apps and application insights for monitoring.
Main,tf
|
|
This is the variable code used for the resource declared.
Variables,tf
|
|
Create a file called provider.tf and insert the following code, so it reaches the provider and configures the state file.
Provider,tf
|
|
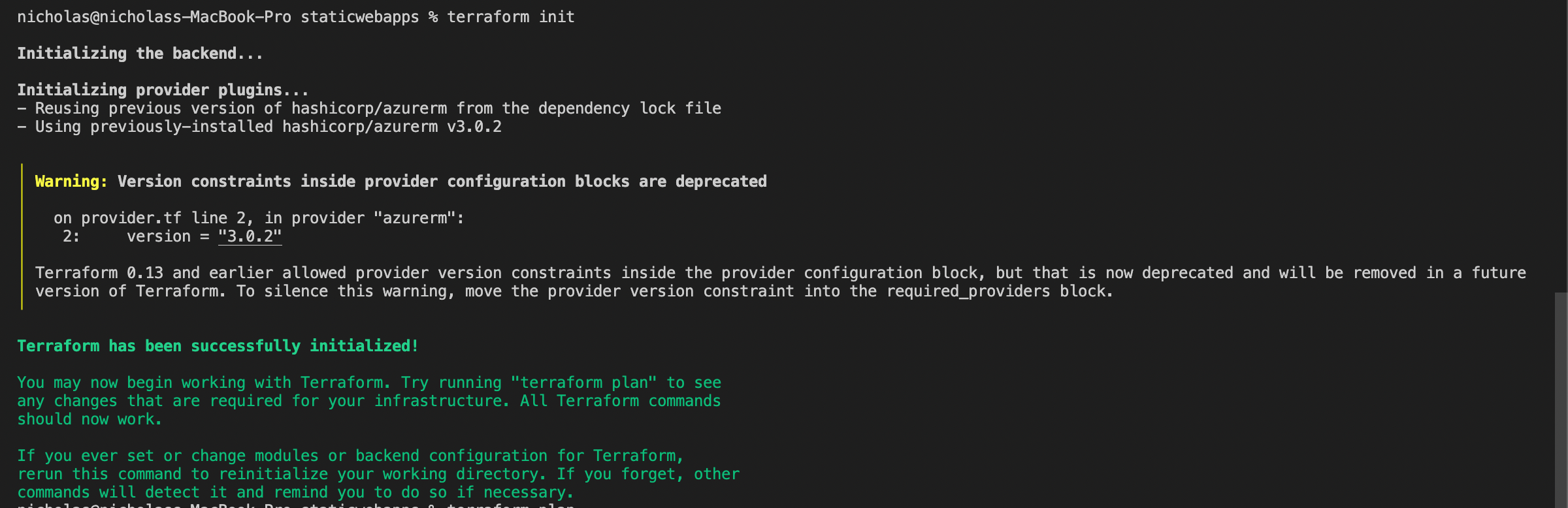
Run terraform init and then terraform plan to ensure the resources and syntax in the preview are correct. If it is successful, you will see a .terraform directory created in your folder.
If you changed the provider or any resources, you must run the terraform init and terraform plan command again.
You will get something like this below.
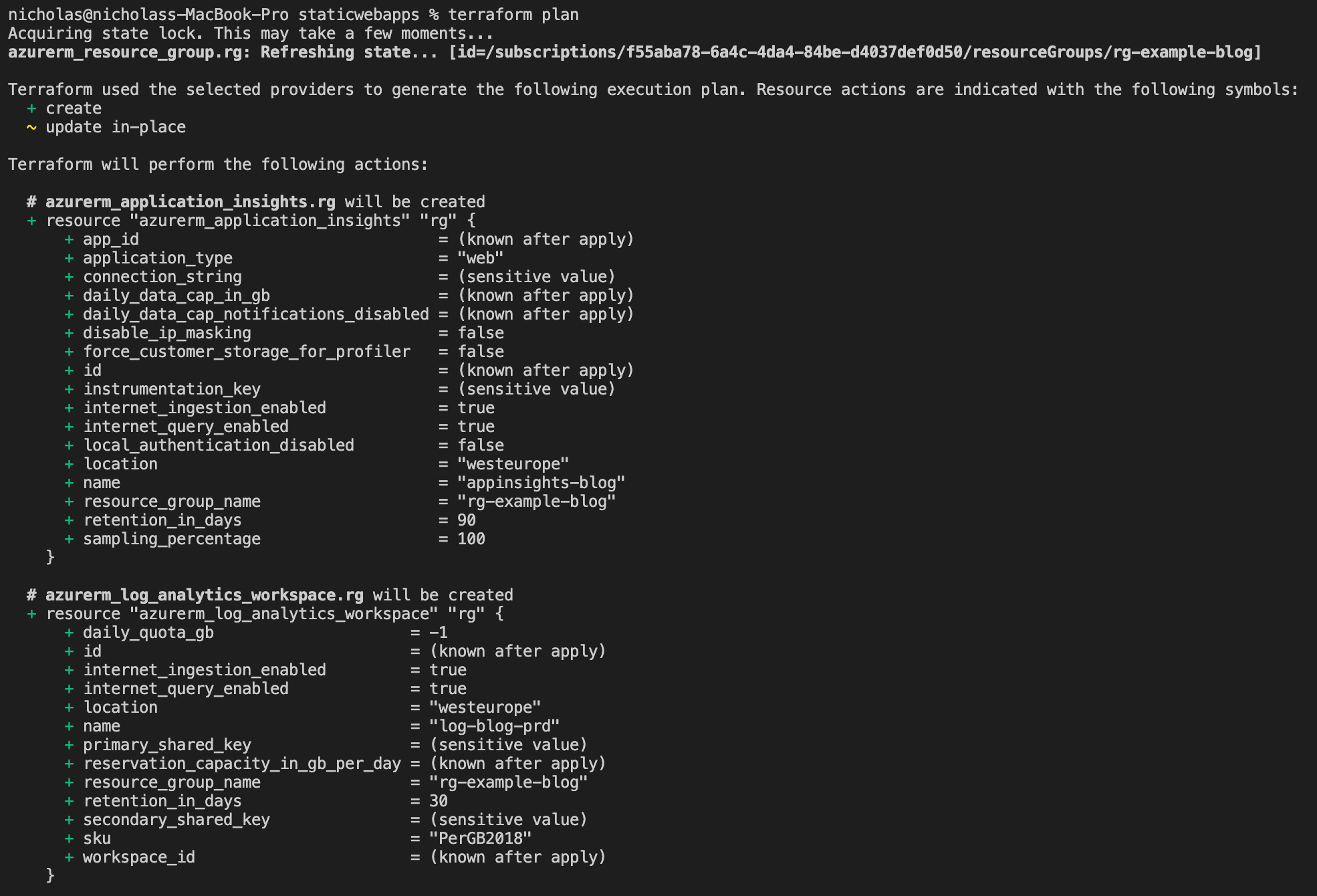
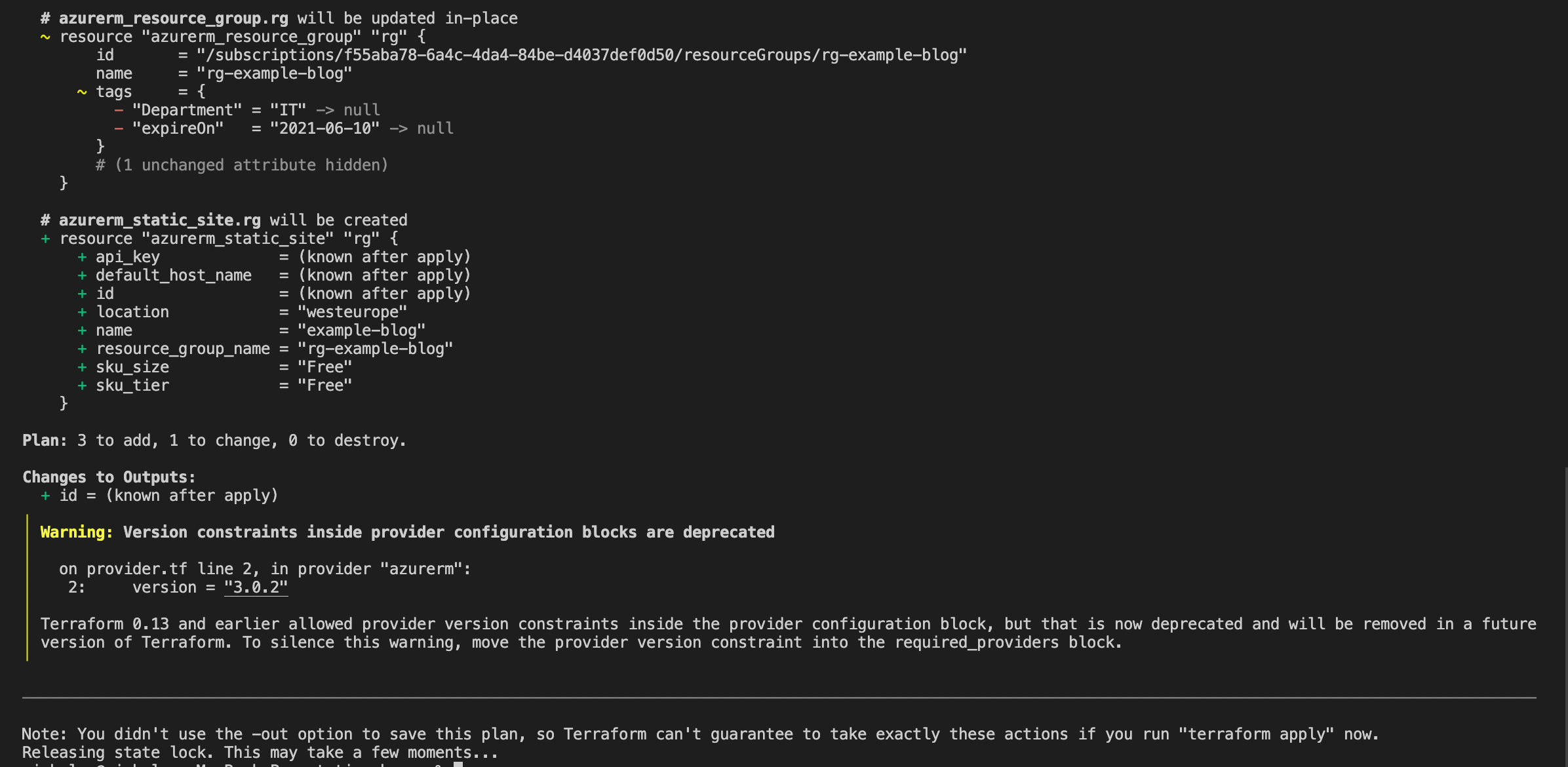
The next step is to run apply to confirm the resources you want to deploy into the infrastructure. It will prompt you to confirm before proceeding. Once confirmed, it should look like the below:
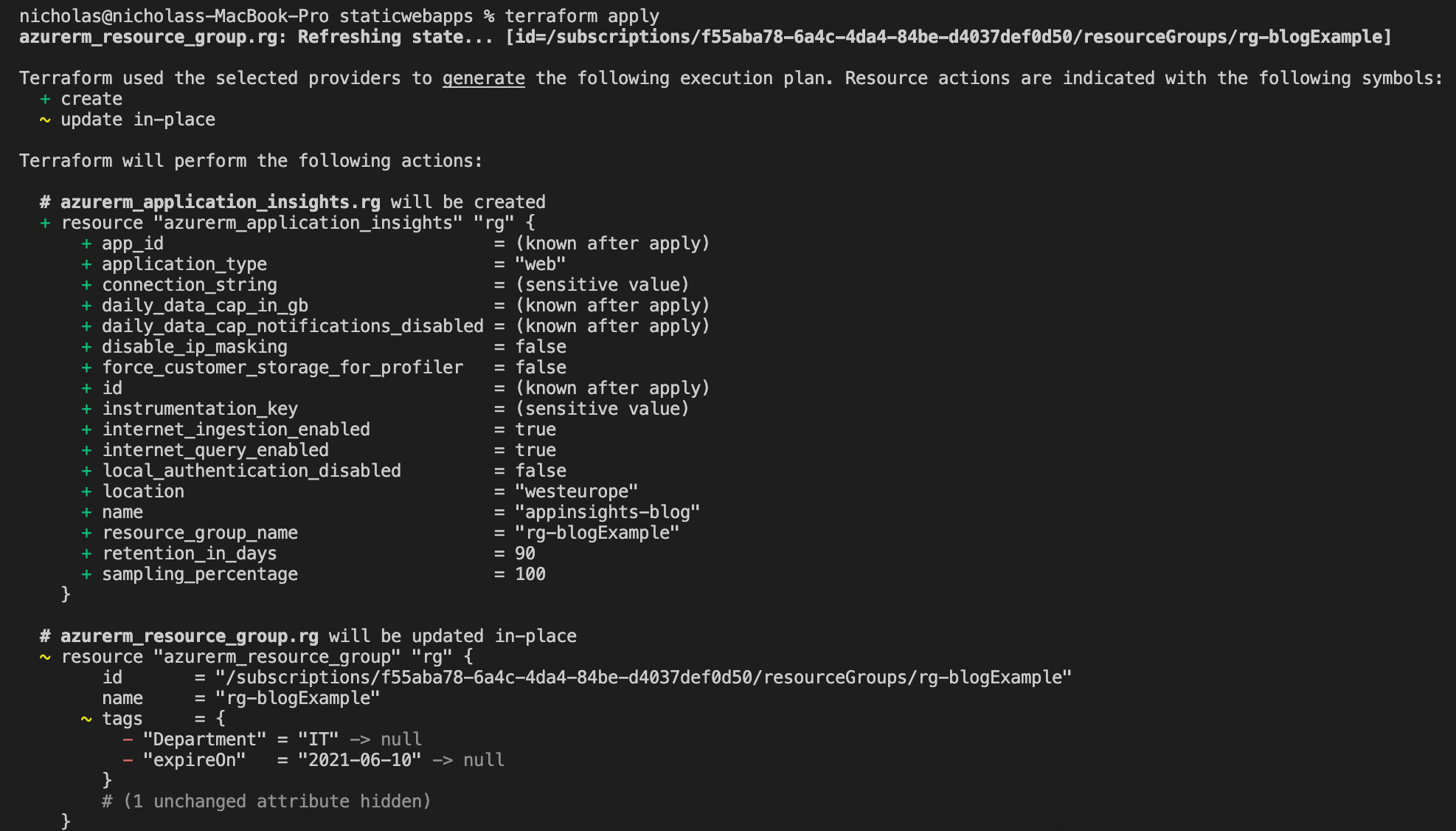
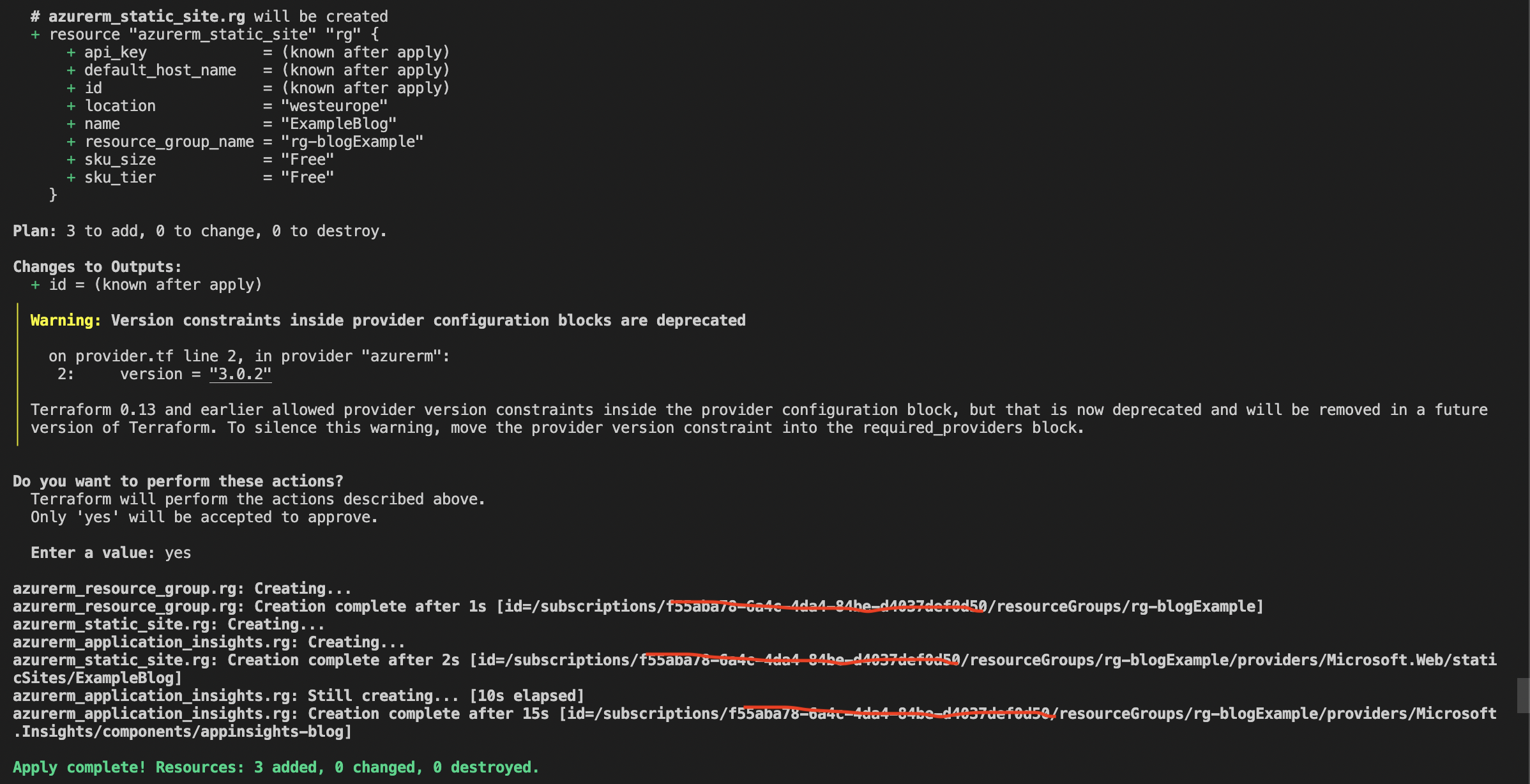
Deployed Azure Resources
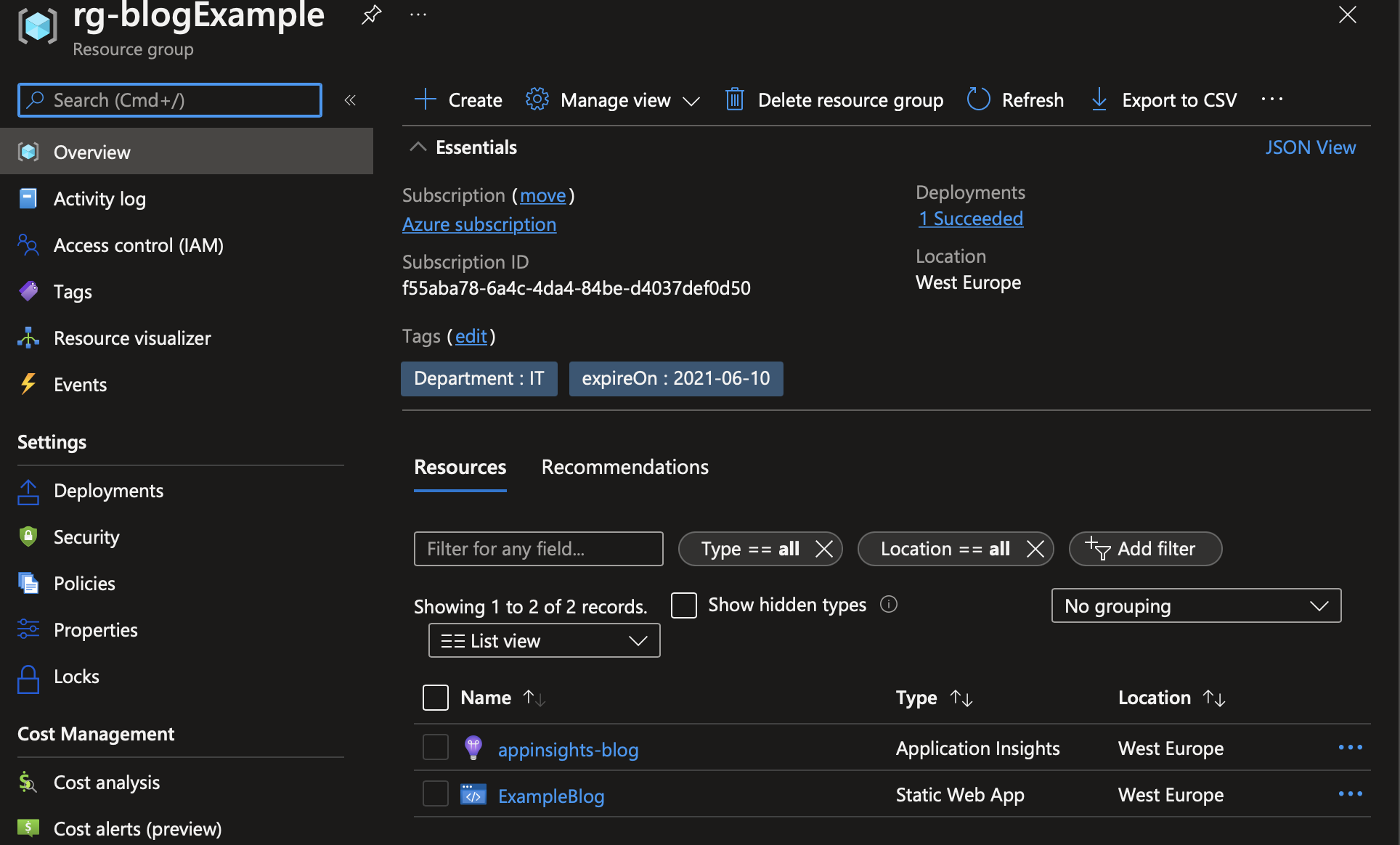
Once it has successfully, it should deploy the resources required into Azure. Head to the Azure portal and find the resource group; you should see the resources inside.
Destroy Resources (Optional)
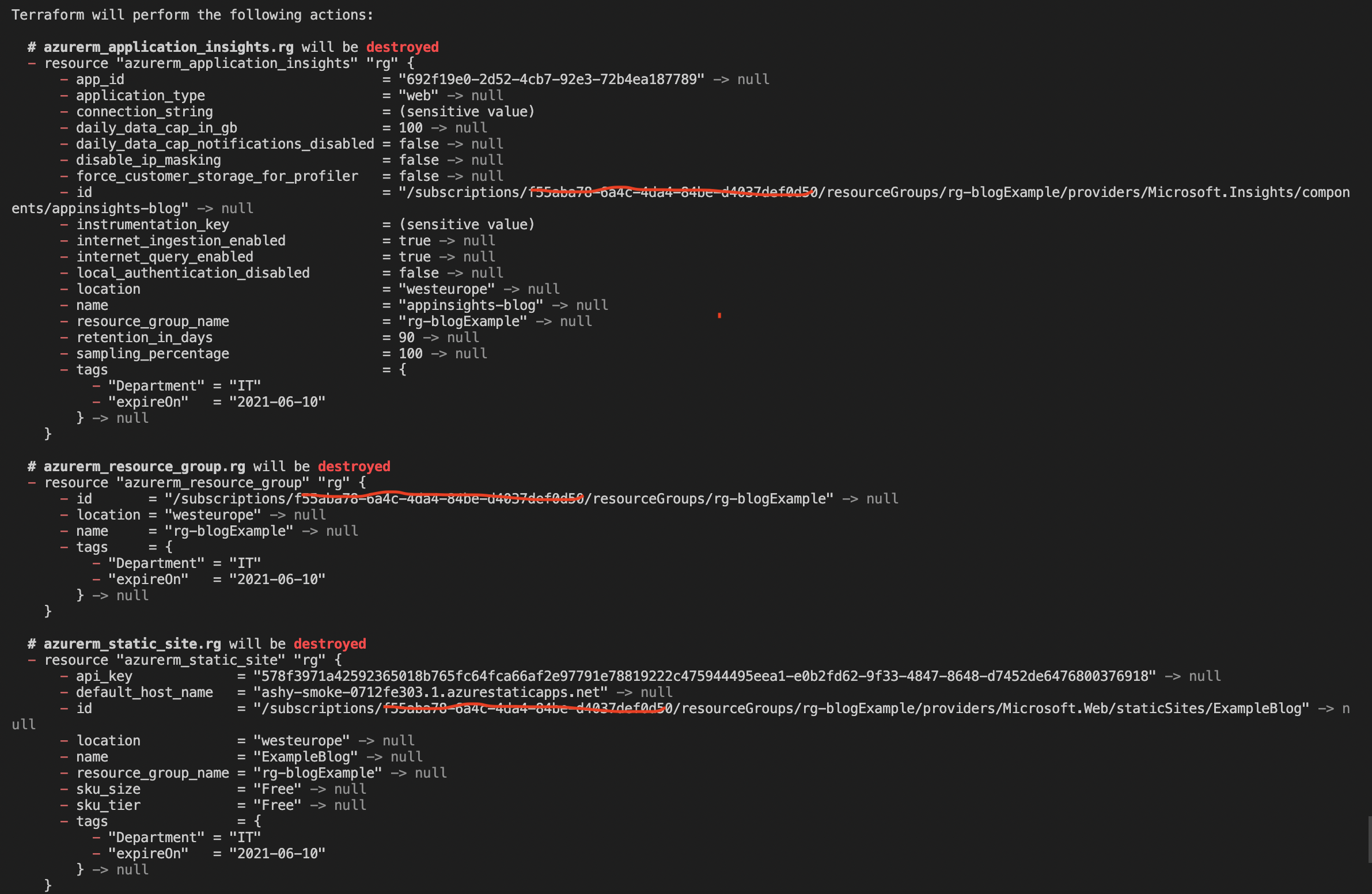
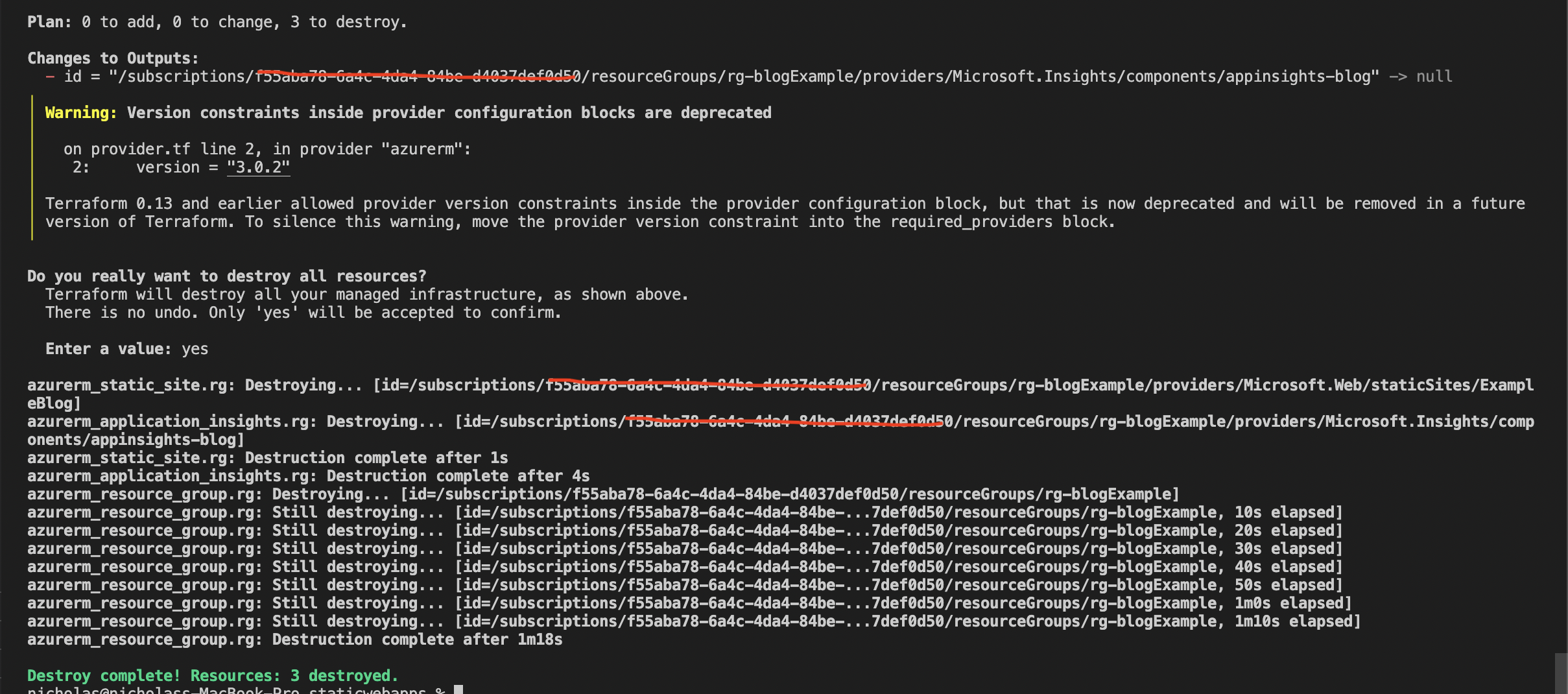
If you want to destroy the resources, you need to run the terraform destroy command.
In this article, we used Terraform to script the creation of an Azure Static web app. We introduced variables and backend in the provider file to deploy the resource.
To Deploy using Azure DevOps, please follow the post on Using Azure DevOps to Deploy Static Web apps

